 |
| |
Carbon Neutral Case Studies |
Global Ecology Center, Stanford, California |
| Building Massing and Orientation
|
The East West Axis
The length of the building is oriented on the dominant east-west passive solar heating axis. As can be seen in the plans, the rooms are distributed along this axis to allow for exposure to the sun to capture heat for the cool months of the year. The benefits of solar gain are optimum with true south exposure.
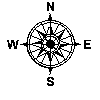
Floor Plan of Level 1 - Ground
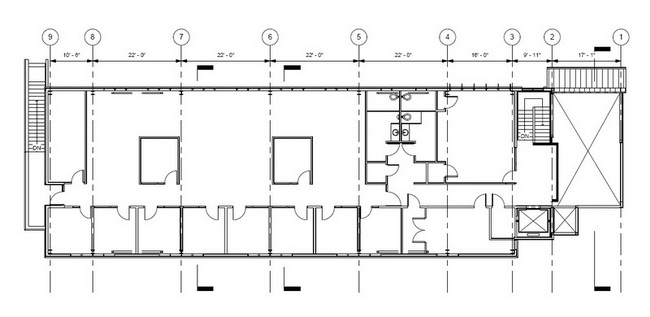
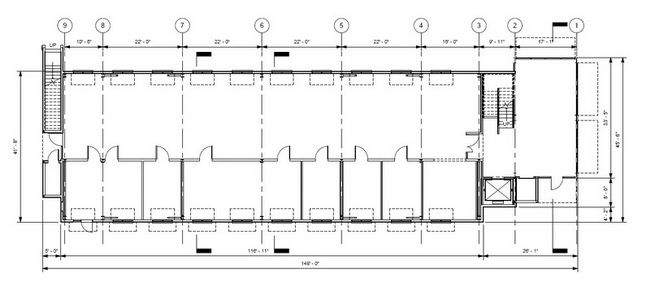
Floor Plan of Level 2 - Second
The building is located on the site an adequate distance from the greenhouse structures to the north as not to cast excess shadows on the structures.
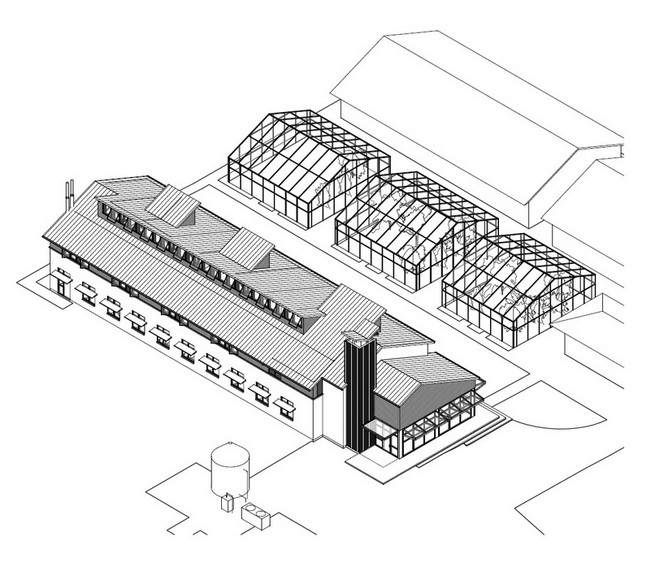
Axonometric Drawing of Building Shown in Context
|

